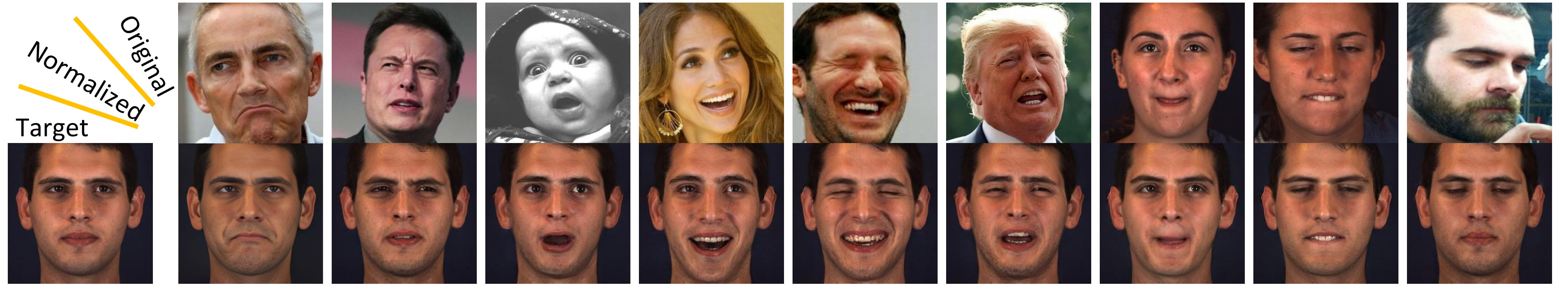

Facial Expression Analysis (FEA) remains a challenging task due to unexpected task-irrelevant noise, such as identity, head pose, and background.
To address this issue, we proposes a novel framework, called Norface, that is unified for both Action Unit (AU) analysis and Facial Emotion Recognition (FER) tasks. Norface consists of a normalization network and a classification network. First, the carefully designed normalization network struggles to directly remove the above task-irrelevant noise, by maintaining facial expression consistency but normalizing all original images to a common identity with consistent pose, and background. Then, these additional normalized images are fed into the classification network. Due to consistent identity and other factors (e.g. head pose, background, etc.), the normalized images enable the classification network to extract useful expression information more effectively. Additionally, the classification network incorporates a Mixture of Experts to refine the latent representation, including handling the input of facial representations and the output of multiple (AU or emotion) labels.
Extensive experiments validate the carefully designed framework with the insight of identity normalization. The proposed method outperforms existing SOTA methods in multiple facial expression analysis tasks, including AU detection, AU intensity estimation, and FER tasks, as well as their cross-dataset tasks.
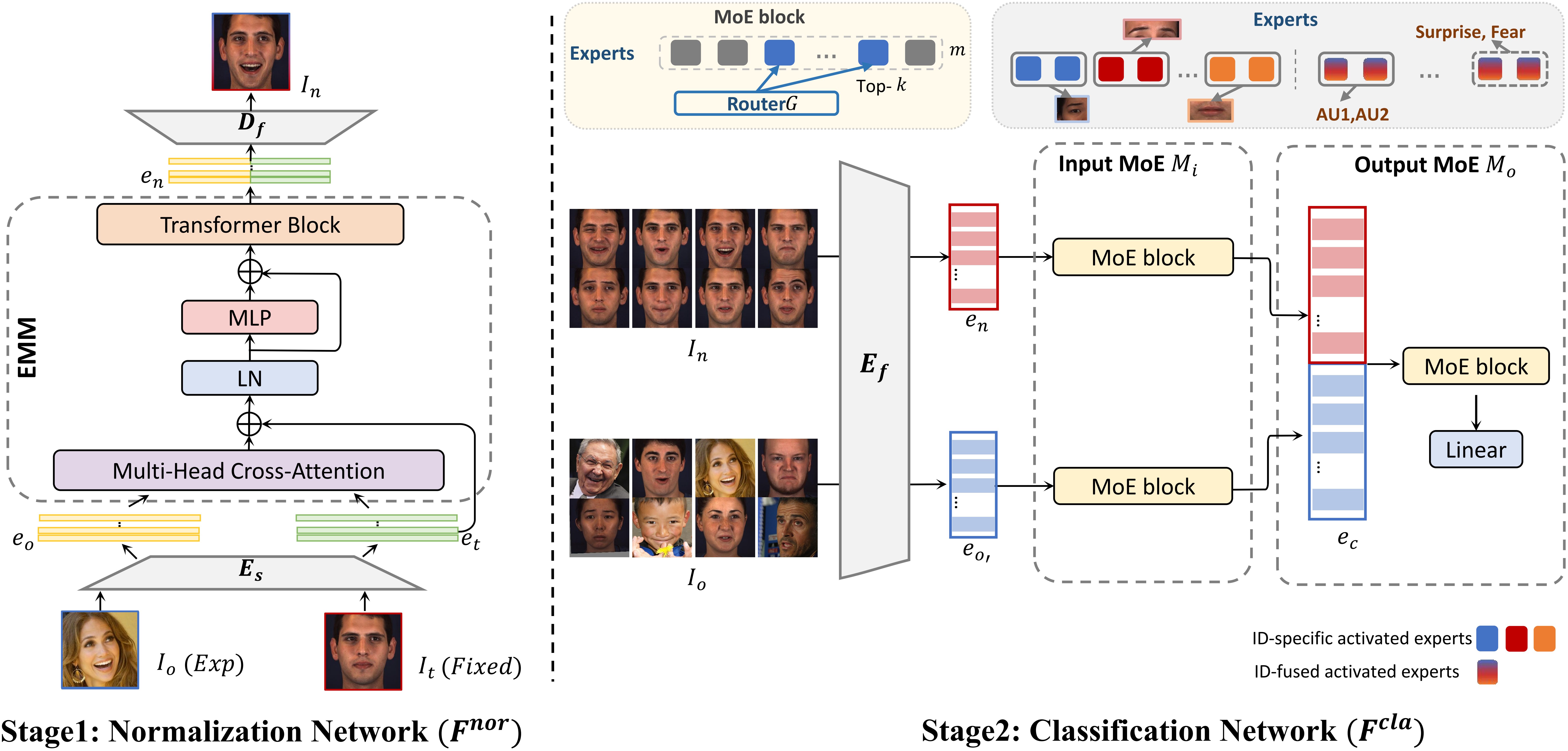 Structure of the proposed Norface. Norface comprises two key stages: identity
normalization and expression classification.
In the first stage, the normalization network
F^nor normalizes all original faces to a common identity with a fixed pose and
background, thereby reducing the influence of task-irrelevant factors. In the second
stage, an Input and Output Mixture of Expert (MoE) based classification network F^cla receives
both normalized and original faces and performs AU detection, AU in tensity estimation, or FER tasks.
Structure of the proposed Norface. Norface comprises two key stages: identity
normalization and expression classification.
In the first stage, the normalization network
F^nor normalizes all original faces to a common identity with a fixed pose and
background, thereby reducing the influence of task-irrelevant factors. In the second
stage, an Input and Output Mixture of Expert (MoE) based classification network F^cla receives
both normalized and original faces and performs AU detection, AU in tensity estimation, or FER tasks.
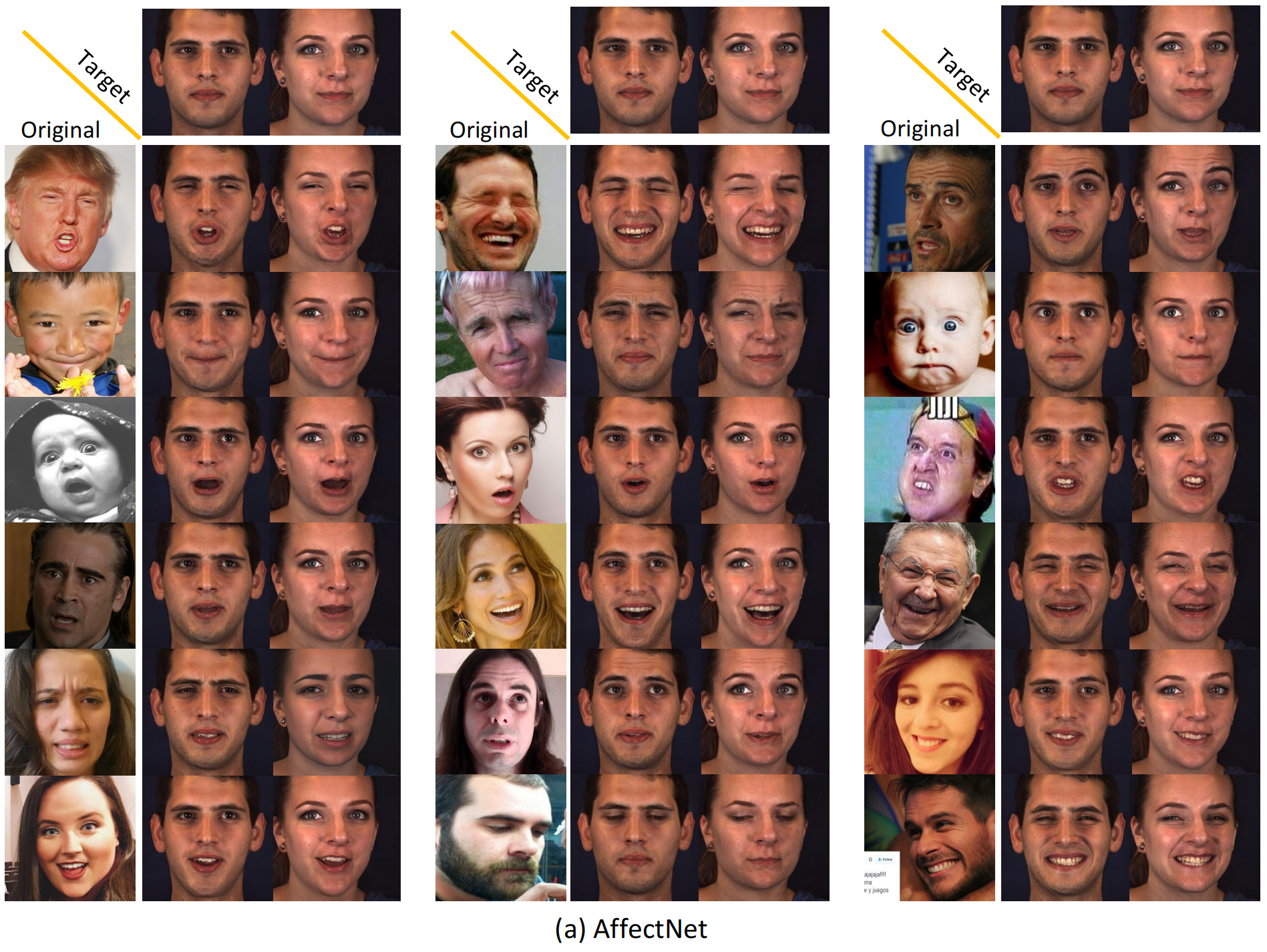
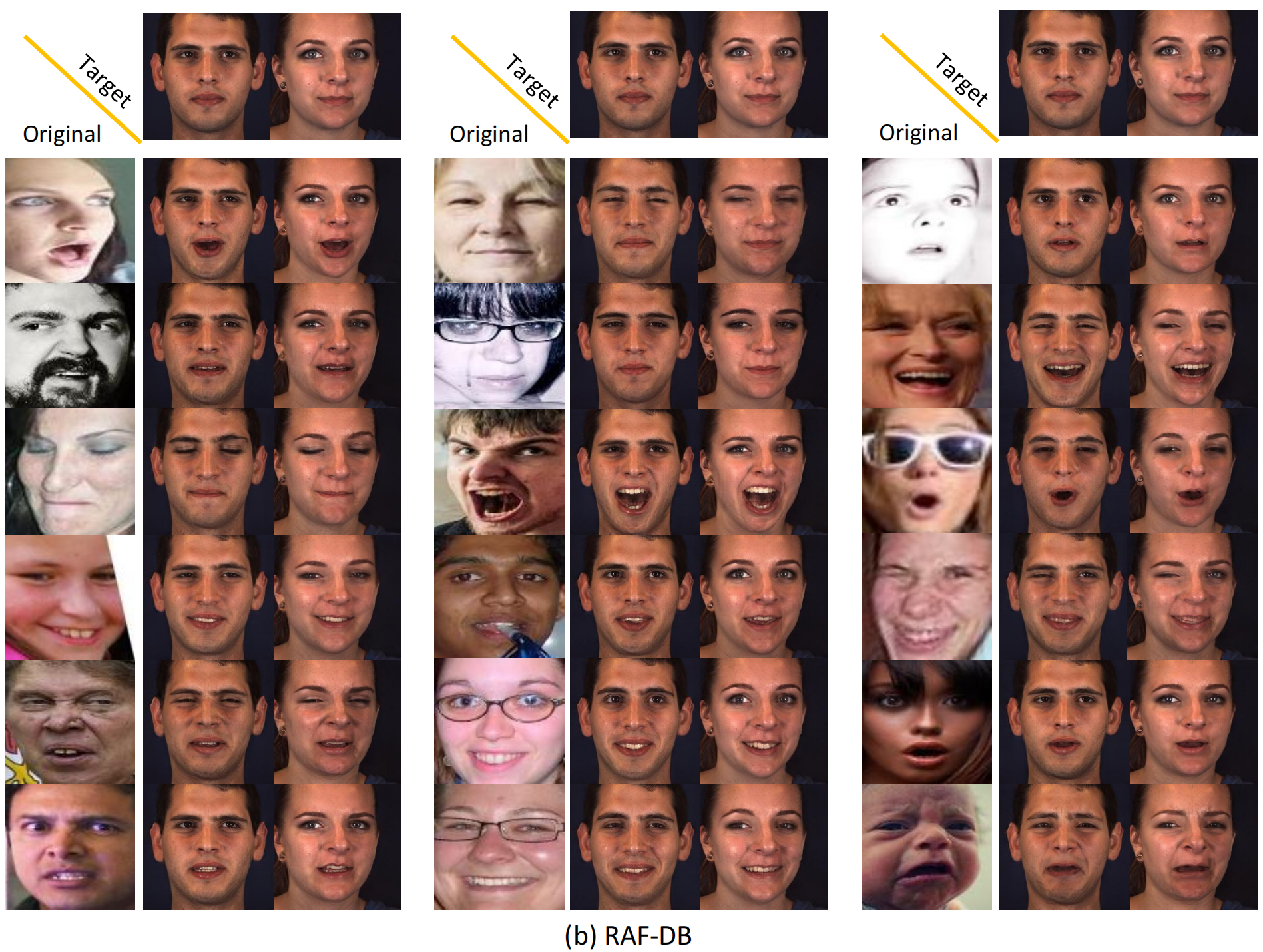


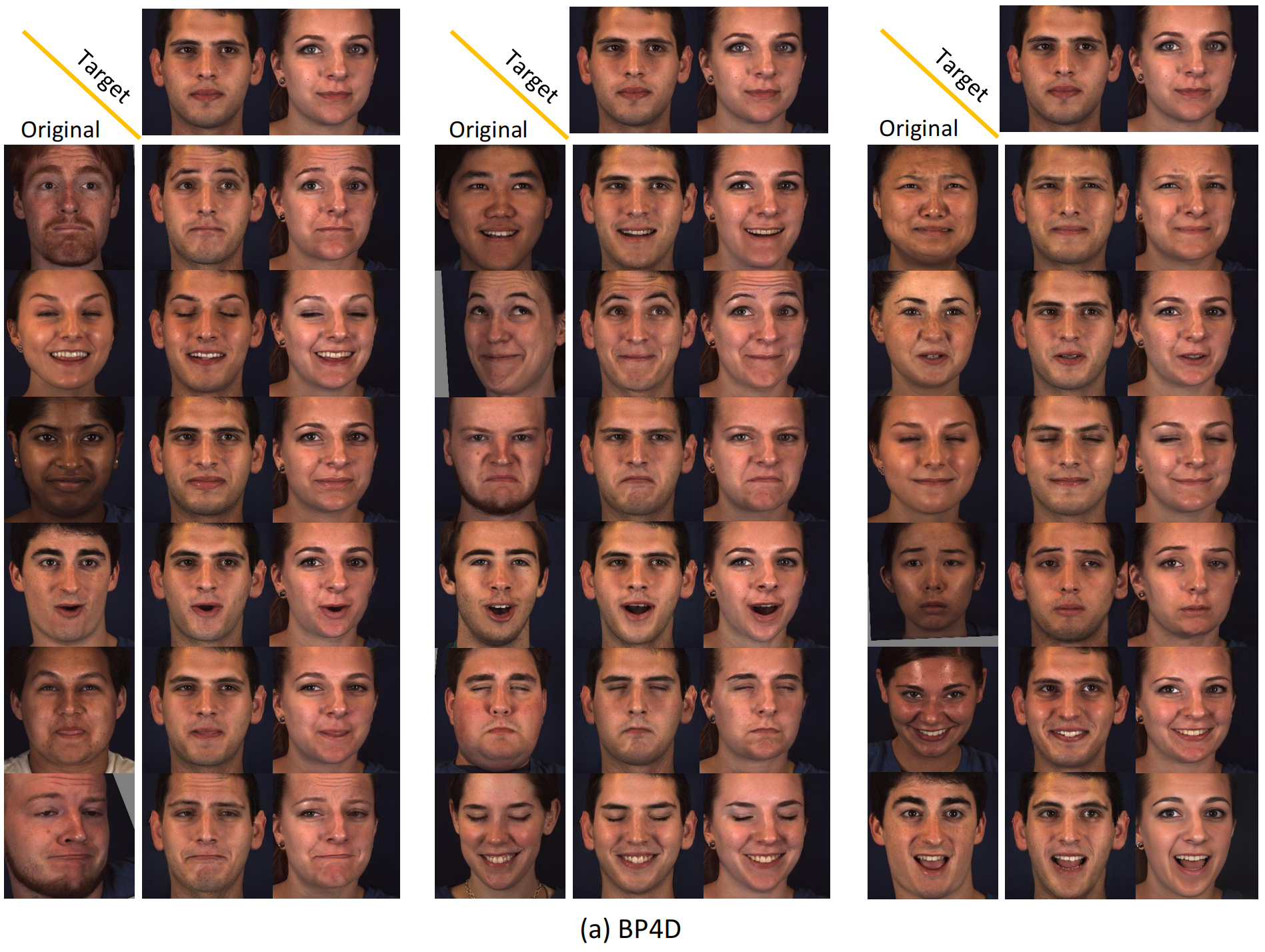
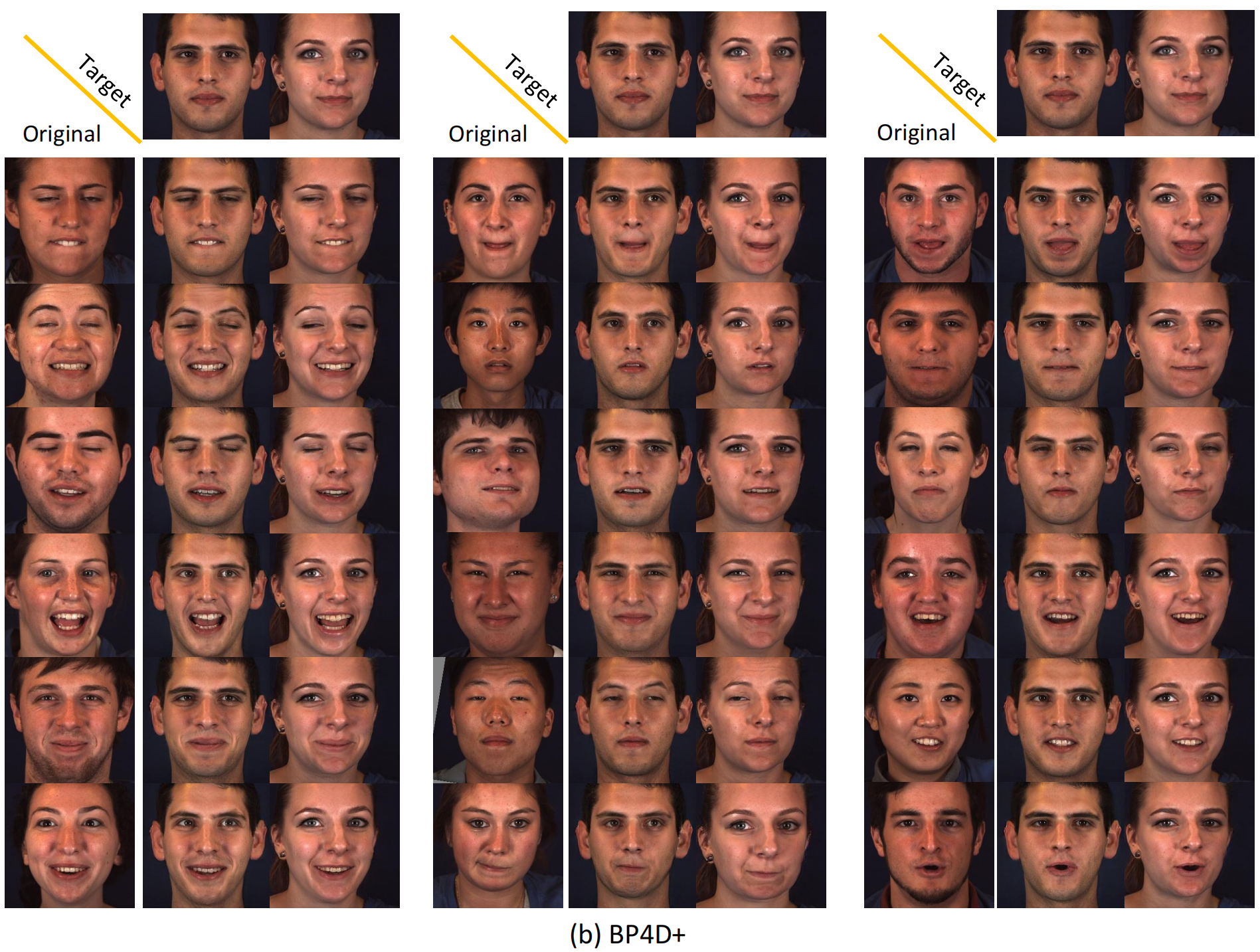

We show several original images that have been normalized to multiple target identities while maintaining consistency in facial expressions.

For the normalized data of all facial expression datasets (AffectNet, RAF-DB, BP4D, BP4D+, DISFA), please visit (Link).
We are actively reaching out to the authors of the BP4D, BP4D+, and DISFA datasets to seek legal permission. Thank you.
For the normalized data of individual facial expression dataset:
1. AffectNet Baidu Cloud (norf).
2. RAF-DB Baidu Cloud (norf).
3. BP4D.
4. BP4D+.
5. DISFA. Baidu Cloud (norf).
If you use our normalized dataset, please cite both our work and the original datasets.
1. AffectNet: Mollahosseini, A., Hasani, B., Mahoor, M.H.: Affectnet: A database for facial expression, valence, and arousal computing in the wild. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing 10(1), 18–31 (2017).
2. RAF-DB: Li, S., Deng, W., Du, J.: Reliable crowdsourcing and deep locality-preserving learning for expression recognition in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 2852–2861 (2017).
3. BP4D: Zhang, X., Yin, L., Cohn, J.F., Canavan, S., Reale, M., Horowitz, A., Liu, P., Girard, J.M.: Bp4d-spontaneous: a high-resolution spontaneous 3d dynamic facial expression database. Image and Vision Computing 32(10), 692–706 (2014).
4. BP4D+: Zhang, Z., Girard, J.M., Wu, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, P., Ciftci, U., Canavan, S., Reale, M., Horowitz, A., Yang, H., et al.: Multimodal spontaneous emotion corpus for human behavior analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 3438–3446 (2016).
5. DISFA: Mavadati, S.M., Mahoor, M.H., Bartlett, K., Trinh, P., Cohn, J.F.: Disfa: A spontaneous facial action intensity database. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing 4(2), 151–160 (2013).
@article{Hanwei2024Norface,
author = {Hanwei Liu, Rudong An, Zhimeng Zhang, Bowen Ma, Wei Zhang, Yan Song, Yujing Hu, Wei Chen, and Yu Ding},
title = {Norface: Improving Facial Expression Analysis by Identity Normalization},
journal = {ECCV 2024},
year = {2024},
publisher = {Springer},
DOI = {10.1007/978-3-031-73001-6_17},
}